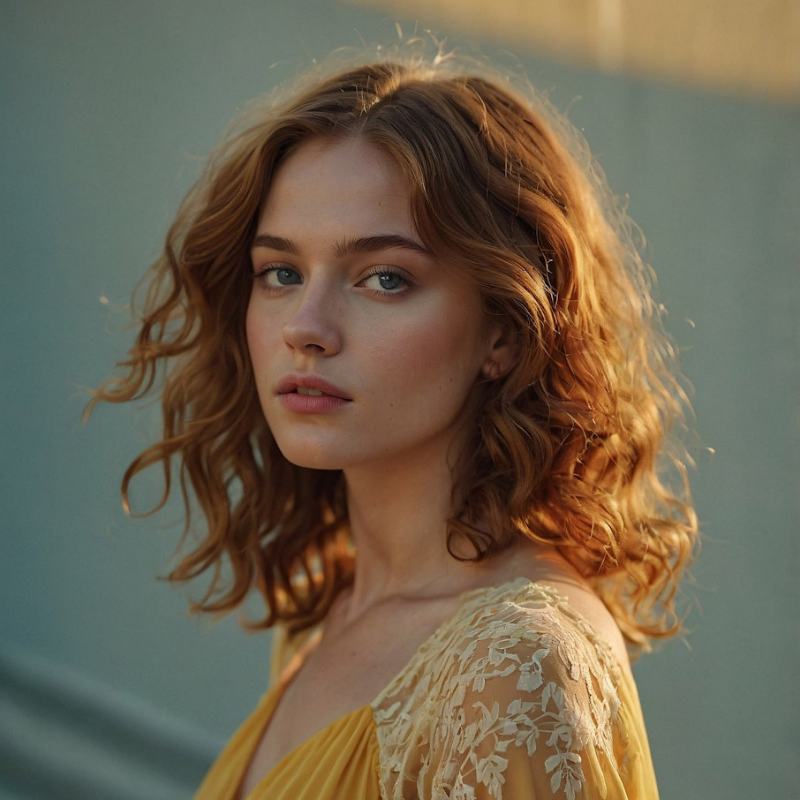
Better Carbs: A guide to low glycemic carbs
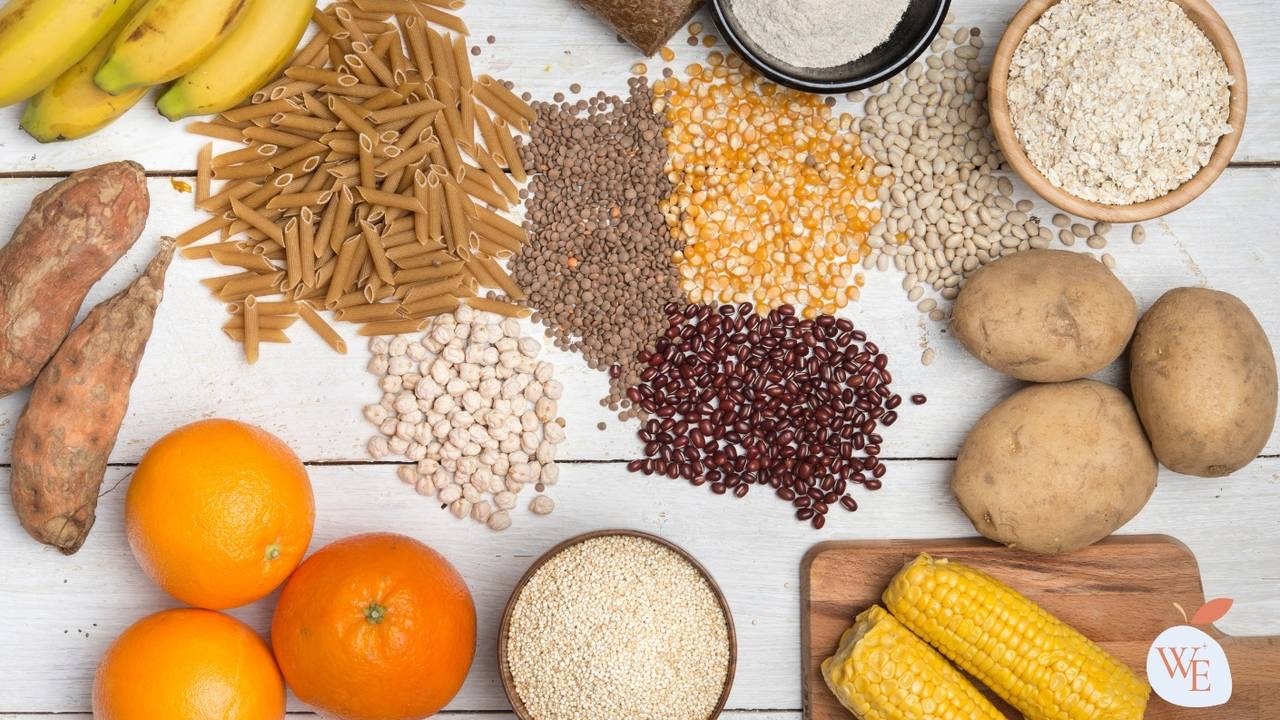

Low glycemic carbs include fruits, vegetables, beans, nuts, and whole grains. These foods are often recommended for people with diabetes because they tend to cause less fluctuation in blood glucose levels.
What are carbs?
A carbohydrate is any food that contains sugar. Carbohydrates provide fuel for our bodies. There are two main types of carbohydrates: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates include sugars like glucose and fructose. Complex carbohydrates contain long chains of sugar molecules called polysaccharides. Examples of complex carbohydrates include breads, pasta, rice, potatoes, beans, and oats. Keep reading for a full breakdown of each.
What are low glycemic carbs?
Low Glycemic Carbs are (complex) carbohydrates that break down into glucose slowly, which means they can curb a spike in blood sugar levels. This type of carbohydrate includes whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, millet, buckwheat, amaranth, teff, sorghum, and wild rice.
Recommended reading: Naturally lower blood sugar with food
Simple carbs
Simple carbohydrates are monosaccharides (single sugar molecules) that are easily absorbed by the body. These include glucose, fructose, galactose, sucrose, lactose, maltose, and dextrins. Simple carbohydrates are often referred to as “simple” because they are not complexed with any other substances. In fact, they are just single sugar molecules.
Simple carbs are sugar. Some occur naturally in foods like milk, but most are added to food.
List of simple carbs
Glucose
Glucose is the simplest carbohydrate molecule. Glucose is the primary source of energy for our bodies. It is the only type of carbohydrate that we produce naturally in our own bodies. Glucose is present in many foods, including fruits, vegetables, milk, and honey.
Fructose
Fructose is a simple sugar that occurs naturally in fruit. Fructose is sweeter than glucose and is commonly used in processed foods and beverages.
Galactose
Galactose is a simple sugar that is found in dairy products. Galactose is sweeter than glucose.
Sucrose
Sucrose is a combination of two simple sugars: glucose and fructose. Sucrose is found in many fruits and vegetables.
Lactose
Lactose is a simple carbohydrate that is found in milk. Lactose is sweeter and less digestible than other types of carbohydrates.
Maltose
Maltose is a simple sugar found in barley, oats, and wheat. Maltose is sweeter than other simple carbohydrates.
Dextrin
Dextrin is a mixture of several different simple carbohydrates. Dextrin is found in corn syrup and molasses.
Complex carbs - the better carbs
Complex carbohydrates are a type of carbohydrate that contains two or more simple carbohydrates bonded together. These types of carbohydrates are not digested as fast as simple carbohydrates, making them ideal for long-term storage. Examples of complex carbohydrates include starches, cellulose, and hemicellulose.
Complex carbs are fiber and starch.
Best low glycemic carbs to add to your diet
These are the best carbs to add to your diet, however, you'll want to combine them with fat and protein to make a whole low glycemic meal. Get some low glycemic recipes and a sample meal plan by downloading our free 5-day meal plan here.
Beans and Legumes
Beans and legumes are excellent sources of protein and fiber. They also contain antioxidants and phytonutrients that help protect against cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
The American Cancer Society recommends eating at least two servings of legumes each week. One serving equals one cup of cooked dried beans, lentils, chickpeas, black beans, split peas, soybeans, or other legumes. You can eat them plain or add them to soups, salads, sandwiches, casseroles, stir-fries, curries, stews, chili, tacos, burritos, enchiladas, and quesadillas.
Whole Grains
Whole grains are rich in nutrients and fiber. They are also high in B vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. However, refined carbohydrates are made by removing some of the bran and germ from whole grains. This process removes much of the nutrition found in whole grains.
The American Heart Association recommends eating at least three servings of whole grains each day. These include brown rice, oats, barley, quinoa, millet, buckwheat, amaranth, teff, sorghum, wheat berries, and wild rice. You should try to eat them every day because they provide many health benefits. For example, whole grains help lower cholesterol levels, reduce risk of diabetes, and protect against cancer.
Recommended reading: 30 foods with a low glycemic index
If you eat oatmeal every morning, you will likely feel better throughout the day because it has a slower effect on blood sugar levels. On the other hand, bread has a faster effect on blood sugar levels, so eating it regularly might make you feel tired and sluggish.
The best thing about oatmeal is that it curbs fluctuating blood sugar levels. In fact, it lowers it. That means you won’t get hungry after eating it, and you won’t be tempted to snack on something unhealthy. Plus, it’s filling and satisfying, which makes it easier to stick to a diet plan.
Sweet Potatoes
You should also consider how much fiber each food contains. Fiber helps keep your digestive system healthy by helping with digestion and preventing constipation. It also helps reduce cholesterol and prevent heart disease.
Nutrition that is found in low glycemic carbs
Brown Rice
Brown rice is a whole grain food that contains many vitamins and minerals. It is high in fiber and low in calories. It is a good source of protein, iron, zinc, vitamin B-6, manganese, copper, niacin, thiamine, folate, pantothenic acid, riboflavin, and selenium. Brown rice is often recommended for people who have diabetes or hypoglycemia.
Quinoa
Quinoa is a seed that is related to spinach and beets. It is gluten free and packed with protein. It is a complete protein containing all nine essential amino acids. It is also rich in dietary fiber, iron, magnesium, phosphorous, potassium, and zinc. It is a great alternative to brown rice.
Oatmeal
Oatmeal is a delicious breakfast cereal that is full of fiber and protein. It is a good way to start your day off right. Oats are also a good source of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. They are high in beta carotene, folic acid, lutein, zeaxanthin, and vitamin E.
Sweet Potato
Sweet potatoes are a root vegetable that is loaded with vitamins and minerals. They are a good source of vitamin A, C, D, K, and E. They are also a good source for fiber, potassium, and manganese.
Whole Grain Bread
Whole grain bread is a healthier option than white bread. It is higher in fiber and lower in sugar content. It is also a good source of protein and iron.
Beans
Beans are a legume that is a good source of fiber, protein, and iron. They are also a great source of folate, magnesium, and potassium.
Lentils
Lentils are a small bean that is a good source for protein, iron, and fiber. They are also a rich source of folate, manganese, and potassium.
Confused what to eat on a Low GI diet?
It’s not as restrictive as you think
Simple recipes using low glycemic carbs
-
Quinoa
- Benefits: High in protein and fiber, gluten-free, and contains all nine essential amino acids.
- Recipe: Quinoa Salad
- Cook 1 cup quinoa according to package instructions. Let cool.
- Mix quinoa with 1 diced cucumber, 1 diced red bell pepper, ¼ cup chopped parsley, and ¼ cup feta cheese.
- Dress with olive oil, lemon juice, salt, and pepper to taste.
-
Sweet Potatoes
- Benefits: Rich in vitamin A, vitamin C, and fiber, with antioxidant properties.
- Recipe: Baked Sweet Potato Wedges
- Slice sweet potatoes into wedges, toss with olive oil, salt, pepper, and paprika.
- Bake at 400°F (200°C) for 25-30 minutes or until tender and golden.
-
Lentils
- Benefits: Excellent source of plant-based protein and fiber, iron, and folate.
- Recipe: Simple Lentil Soup
- Sauté 1 chopped onion, 2 minced garlic cloves in olive oil until soft.
- Add 1 cup lentils, 4 cups vegetable broth, 1 diced carrot, and 1 diced celery stalk. Simmer until lentils are tender.
- Season with salt, pepper, and a pinch of cumin.
-
Chickpeas
- Benefits: High in protein, fiber, and several vitamins and minerals.
- Recipe: Chickpea Salad
- Combine 1 can drained chickpeas, 1 diced cucumber, 1 diced tomato, and ¼ cup chopped parsley.
- Dress with olive oil, lemon juice, salt, and pepper.
-
Barley
- Benefits: Good source of fiber, can help lower cholesterol, and rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Recipe: Barley and Vegetable Soup
- Cook 1 cup barley as per package instructions. Set aside.
- In a pot, sauté 1 chopped onion, 2 minced garlic cloves, 2 diced carrots, and 2 diced celery stalks.
- Add 6 cups vegetable broth and cooked barley. Simmer until vegetables are tender. Season with herbs.
-
Oats
- Benefits: High in beta-glucan fiber, which helps lower cholesterol and control blood sugar levels.
- Recipe: Overnight Oats
- Mix ½ cup rolled oats with ¾ cup almond milk, 1 tbsp chia seeds, and 1 tbsp maple syrup.
- Refrigerate overnight. Top with fresh berries before serving.
-
Black Beans
- Benefits: Rich in protein, fiber, and antioxidants, supports heart health.
- Recipe: Black Bean Tacos
- Mash 1 can black beans and season with taco seasoning.
- Serve on corn tortillas with lettuce, diced tomatoes, and shredded cheese.
-
Bulgur
- Benefits: High in fiber and protein, quick cooking, and supports healthy digestion.
- Recipe: Tabouli Salad
- Soak 1 cup bulgur in hot water for 30 minutes. Drain and squeeze out excess water.
- Mix with diced tomatoes, cucumber, green onions, parsley, mint, lemon juice, olive oil, salt, and pepper.
-
Brown Rice
- Benefits: Rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, supports blood sugar control.
- Recipe: Brown Rice Stir-Fry
- Cook 1 cup brown rice. Sauté your choice of vegetables (broccoli, bell peppers, carrots) and tofu in soy sauce and garlic.
- Mix with cooked rice and serve hot.
-
Whole Grain Pasta
- Benefits: Higher in fiber and nutrients than white pasta, supports energy levels.
- Recipe: Whole Grain Pasta with Vegetables
- Cook whole grain pasta according to package instructions. Sauté garlic, spinach, cherry tomatoes, and zucchini in olive oil.
- Toss cooked pasta with the sautéed vegetables and top with grated Parmesan cheese.
Each of these recipes incorporates a low glycemic, complex carbohydrate that can help maintain stable blood sugar levels, making them great choices for anyone looking to improve their dietary habits.
Frequently asked questions about low glycemic carbs
-
What are low glycemic carbohydrates?
- Low glycemic carbohydrates are foods that have a minimal impact on blood glucose levels. The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly food causes our blood sugar levels to rise. Foods with a low GI (55 or less) are digested, absorbed, and metabolized more slowly, causing a slower and smaller rise in blood sugar levels.
- What are the best low glycemic carbs?
- Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, oats, barley, millet, buckwheat, amaranth, teff, sorghum, wild rice, and beans such as black beans, lentils, chickpeas, adzuki beans, navy beans, pinto beans, kidney beans, lima beans, soybeans, mung beans, and fava beans.
-
Why are low glycemic carbs important?
- Low glycemic carbs are important because they help manage blood sugar levels, which is crucial for people with diabetes, prediabetes, or those looking to maintain a stable energy level throughout the day. They can also help with weight management, as they tend to keep you feeling fuller for longer and may reduce the likelihood of overeating.
-
Can eating low glycemic foods help with weight loss?
- Yes, incorporating low glycemic foods into your diet can aid in weight loss. These foods can help control appetite and delay hunger cues, which can prevent overeating. By promoting better blood sugar control, low glycemic foods can also help reduce cravings for sugary snacks, making it easier to stick to a healthy eating plan.
-
What are some examples of low glycemic carbs?
- Examples of low glycemic carbs include most fruits and vegetables, legumes (such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas), whole grains (like oats, barley, and quinoa), nuts, seeds, and dairy products with low levels of fat. These foods not only have a low GI but also provide essential nutrients and fiber.
- Are eggs a low glycemic food?
- Eggs contain no carbohydrates, so they don't raise blood sugar levels like other high carbohydrate foods do. This means that if you eat eggs regularly, you won't experience any insulin spikes.
-
How can I incorporate low glycemic carbs into my diet?
- Incorporate low glycemic carbs into your diet by choosing whole grains over refined grains, opting for fresh fruit instead of fruit juice or dried fruit, and including legumes in your meals. You can also replace high GI foods with lower GI alternatives—for example, using sweet potatoes instead of regular potatoes or quinoa instead of white rice. Planning meals and snacks around these choices can help ensure a balanced intake of low glycemic carbs.
You Might Also Like:
Feeling down about your weight and not really sure what’s wrong? You’re eating healthy and working out, but nothings really changing… try the 5-day meal plan featuring easy and familiar foods. Discover the simplicity of low glycemic living and finally release the weight and feel 10x better in your body.